A Complete Guide on Cloud-Based Application Development
Modern applications cope with tremendous computing power, and businesses managing them seek out cloud application development for their projects. However, choosing the right solution requires an understanding of how the industry works and what its variables can be. So today, we’d like to share JetBase’s experience on this subject.
With almost a decade on the market, we’ve learned all about cloud apps and how to make them efficiently without any compromises on quality. In this article, we will discuss the types of cloud solutions and their benefits for your company. Precisely, we’ll take you through the cloud application development process in stages, explaining the importance of each one, and discuss the cost of cloud application development and ways to reduce it.
We’ll round off with tips on addressing the challenges that could arise during cloud app development. This should give you a good primer on the state of the market and the ways you can approach cloud application development. Without further ado, let’s get started with JetBase’s guide to cloud app development.
What Is a Cloud-Based Application?
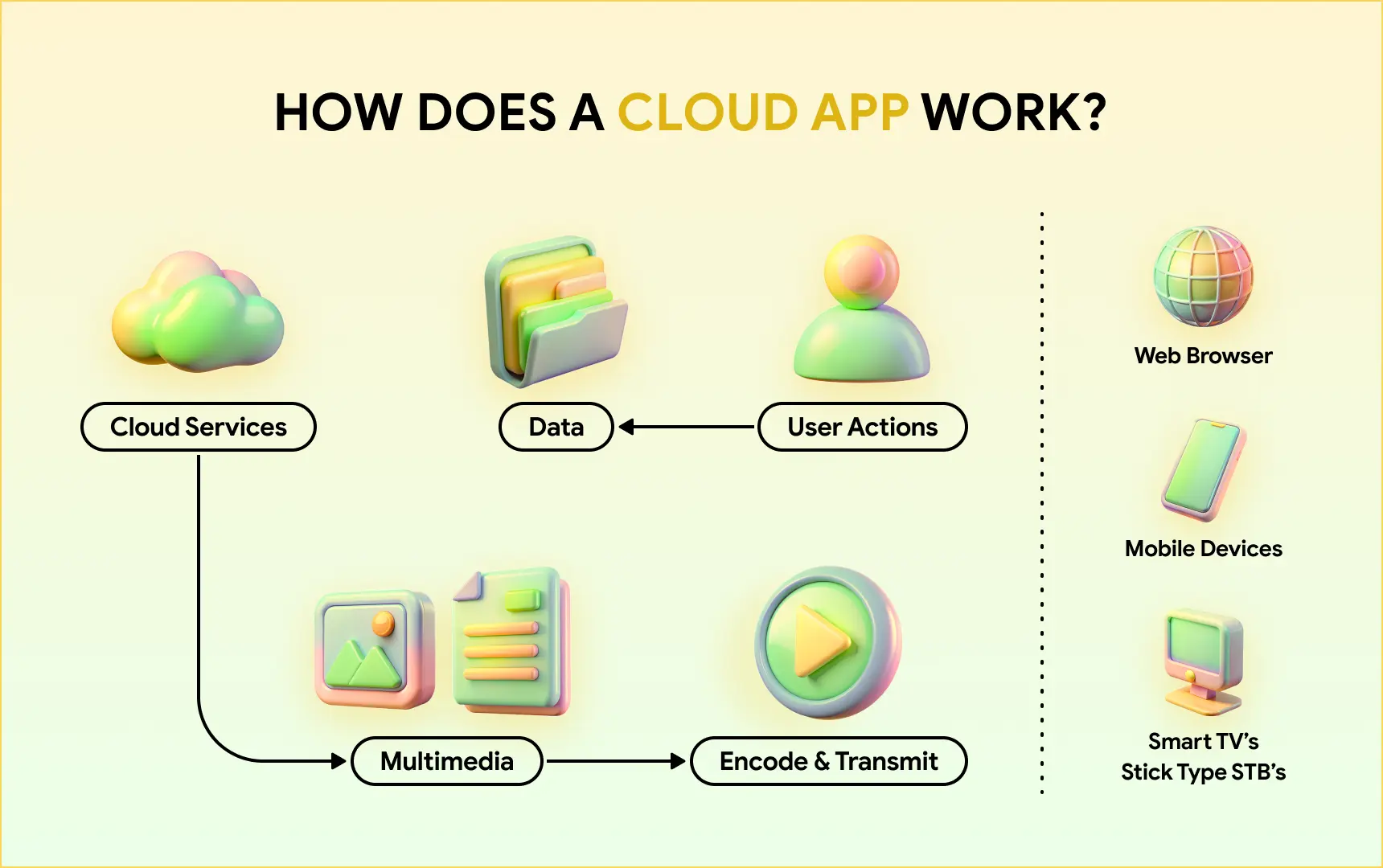
A cloud app is an application that functions using remote (also known as cloud) servers. Users interact with them through browsers on desktop or mobile devices, and APIs handle the communication between these devices and servers.
Cloud apps’ unique structure allows them to:
- Provide faster responses to user inputs
- Scale up or down depending on the number of concurrent users
- Reinforce data security
- Use interconnected APIs
Being more prominent in cloud applications development than in non-cloud architecture, such features are lucrative for companies that want a quality solution with some extra positives. In particular, they let businesses avoid direct server management, speed up cloud application development, and require less manpower post-launch. Also, not having to run your own servers means fewer expenses and no need to devote extra space to the hardware infrastructure.
While non-cloud apps were once the norm, the market for cloud apps has recently grown substantially and will only keep expanding. As a result, it becomes safer to say that the cloud is taking over, with giants like Microsoft and Google investing in their own cloud services.
Key Statistics of Cloud Applications Development:
- By 2026, the cloud computing market is forecast to be worth $947.3 billion.
- Amazon Web Services remains the biggest public cloud provider, with 32% of the market.
- 96% of companies use the public cloud.
- 84% of companies use the private cloud.
- By 2025, there will be 200 zettabytes (a trillion gigabytes) of data in the world.
- The main challenge facing cloud decision-makers is managing cloud spend (82%).
- 94% of businesses noted improvements in their security after moving to the cloud.
These solutions look more and more preferable, given the plenty of computing power, fault tolerance, and security measures they handle. However, it’s not just about the financial aspect and convenience. There are several different cloud app options you can choose from, making cloud apps customized to your business needs.
How Does a Cloud App Work?
3 Types of Cloud Solutions for Enterprises
There are three key types of cloud apps you can choose from to develop cloud application plans.
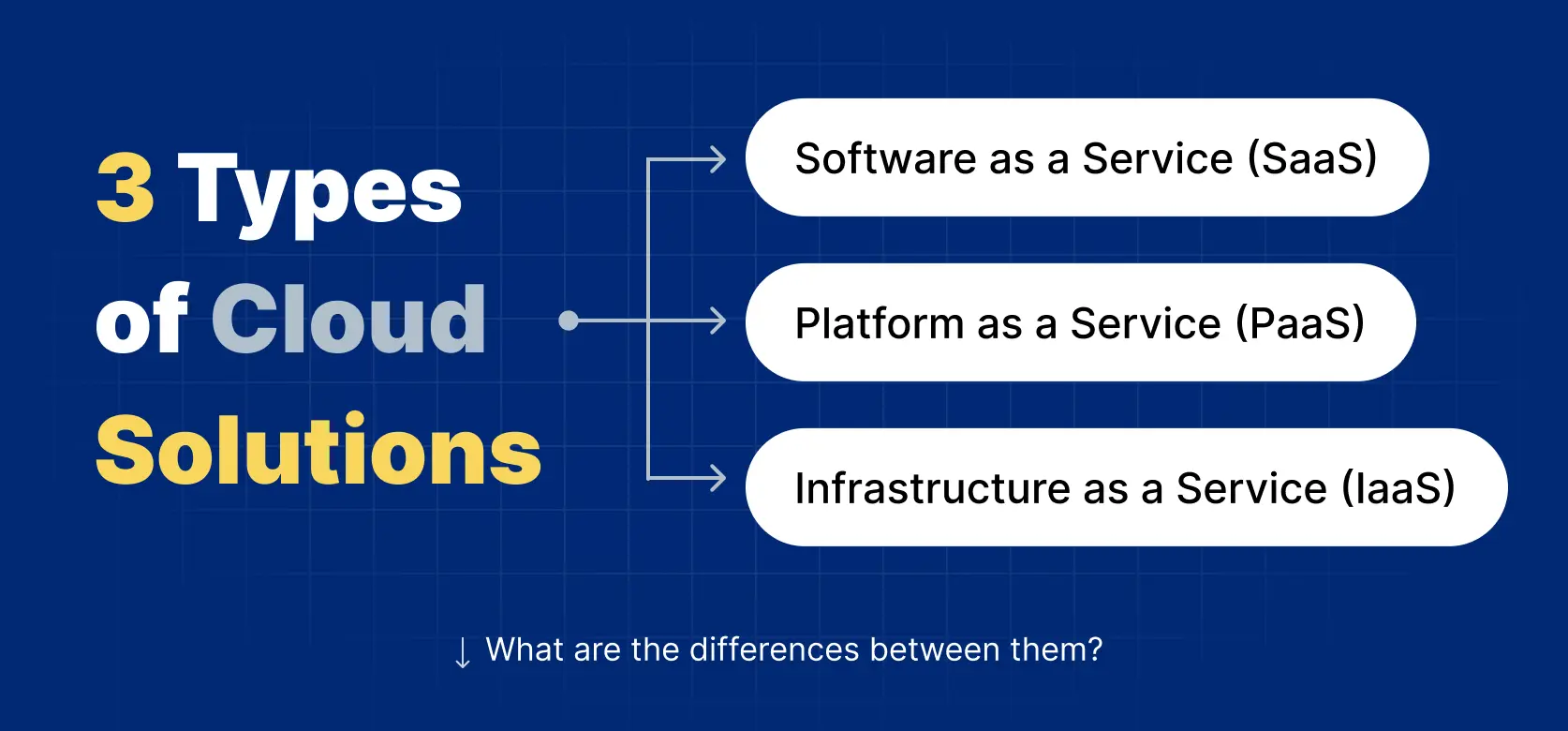
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is run on servers that don’t belong to the company that made that software. In practice, it means you can access SaaS from anywhere – with any device and without the need to install it.
Oftentimes SaaS is considered synonymous with cloud apps in general, as it’s by far the most well-known type of cloud solution. The prominent SaaS types include:
- CRM (customer relationship management) software;
- Salesforce;
- Hubspot solutions.
Adobe Creative Cloud is also an example of cloud based app development. That’s a good example of a giant corporation relying on external cloud servers for its solutions, which are then used by millions of customers.
SaaS helps companies by offering them access to complex, highly customizable tools without having to develop and maintain them. It’s one of the most commonplace cloud app types for a reason. Convenience and cost efficiency are hard to beat here, especially on an enterprise scale.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Let’s say you want to create a truly innovative cloud application but don’t have the necessary hardware and tools. This is where PaaS comes in, as a company can simply rent software and hardware resources for cloud app development.
PaaS is perfect for decentralized cloud application development with many collaborators. The cloud provider takes care of the maintenance while you create.
PaaS is traditionally used by smaller companies that may not have the capital to buy the necessary tools and hardware. However, that doesn’t mean that enterprises can’t rely on it too. A platform like Windows Azure has enough computing power and features to replace physical environments completely, even when it comes to an enterprise.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
A step up from PaaS, IaaS implies everything about your infrastructure is in the hands of your cloud provider. The network, the servers, the databases, and even the visualization are all processed through the cloud. As a result, you reduce overhead costs substantially while getting all the right tools to develop cloud based application.
With IaaS, you get:
- security layers (PCI-DSS compliance, complete data encryption);
- load balancing;
- clustering features.
They all come pre-made, not only speeding up development but guaranteeing they’ve been time-tested. As a result, a lot of small and mid-size companies turn to IaaS for their cloud app development needs.
We don’t necessarily consider this the most relevant type for enterprises, as they can typically run their own infrastructure easily enough. It is, however, potentially a bit more budget-friendly. Plus, with the ability to run IaaS on a private cloud, it can be a viable option even at this level.
With these three types explained, you should have a grasp of which one is the most relevant to you. However, before we proceed to talk about the cloud applications development stages, we’ll quickly address why cloud app development is worth it.
When to Choose SaaS, PaaS or IaaS?
The SaaS platform suits teams who require pre-packaged tools that need little customization for operations such as CRM and project management.
You should select PaaS when you need to build a custom application and accelerate development while avoiding infrastructure management responsibilities.
Select IaaS when you require complete infrastructure control and scalability features together with custom deployment capabilities.
Key Benefits of Cloud-Based Applications
In this section, we highlight all the general advantages of cloud based app development in return for your time and money investment.
Cost Efficiency
When your app runs on a cloud service, you pay only for what you use. Spending money on the essentials helps you quickly offset the initial investment you make.
The convenience of having easy, instant access to your data and features will inevitably end up saving you money. You won’t be constantly dealing with:
- Errors;
- Downtime;
- prolonged maintenance.
As a result, your operations will be more efficient and, thus, cost-effective.
Security
Despite some apprehensions that you might have when handling so much control over the cloud provider, security is actually an advantage for cloud apps.
When you choose to develop cloud application solutions, the security of your system is the responsibility of the provider. Therefore, they put a lot of resources into encryption and compliance with security standards.
Flexibility
Flexibility applies to what you can make with more powerful and unique features in cloud based application development. It’s also applicable in terms of bandwidth use, as you can easily scale it up based on your needs.
Plus, it’s also flexible in terms of your time, freeing up your team to focus on cloud application development instead of any server maintenance or deployment.
Sustainability
The aforementioned higher bandwidth, as well as the general computing power that comes with cloud services, opens up a lot of potential. Thus, developing cloud applications is a good way to secure your business in the future.
With some new technologies, such as AI and LLM, requiring substantial computational power to run and train, the cloud is the way of the future.
Step-by-Step Process for Developing a Cloud Application
This section goes through the stages of the cloud based app development process and shows how to navigate its complexity. Use these tips from our personal experience to make things easier in cloud applications development.

Step 1: Researching the Market and Requirements
As in any sphere, planning and proper analysis are key to your future success. By understanding the market, you can gauge interest in your cloud application and see if a pivot might be in order. Having a clear picture of what’s missing on the market and what’s oversaturated will help you invest smarter.
Research lets you know who your real target audience is, how to market your cloud application to them, and which course you should take in terms of:
- UI/UX design;
- platform choices;
- features.
It basically dictates what your app will look like and whether it will be sustainable. This way, doing the research means you won’t have to spend time and money iterating and trying to find the right way to make your cloud application. It will be dictated to you by the market.
Step 2: Hiring Developers
Once you have a full understanding of the final product, it’s time to get the people who will bring that picture to life. For this, you can take one of three approaches:
- Staff an in-house department
- Hire freelancers on a short-term contract
- Outsource cloud application development to a vendor
An in-house cloud applications development department guarantees you will have post-release support and can integrate these devs with the rest of your company. That helps build trust and understanding, which can lead to high-quality work. However, the downsides are onboarding and operational expenses associated with hiring new people long-term.
With freelancers, you eschew the maintenance costs but run the risk of possible inaccessibility when their consultations and work may be needed. Plus, depending on the platform you use and the experience you have, the lack of proper vetting can lead to hiring unskilled developers. You can probably guess what that results in and why it’s crucial to verify any candidate’s experience.
As for outsourcing, you can arrange long-term collaboration and have a team of verified experts doing your project. However, problems can stem from communication or lack thereof. Depending on the region you hire from, your team may be in a drastically different time zone and thus struggle to sync up with you. Plus, cultural clashes could lead to slower cloud application development and general unhappiness among the team.
As you can see, there isn’t one perfect choice, and each approach requires care and patience. That will help deal with many of these problems and leave you with a good, smooth
![Cloud Software Development [AWS].webp](/static/Cloud_Software_Development_AWS_a351611d38.webp)
Step 3: Choosing Tech Stack
Ideally, you can simply defer to your dev team on this, and they will help pick the optimal technologies for your cloud based application development. Regardless of whether you trust your team or prefer to pick yourself, consulting with developers on the tech stack is crucial. Choosing your architecture means determining the future of your cloud app development and what it can offer users.
Here is a table summarizing some of the most popular tech stack options for cloud application development, categorized by programming languages, databases, frameworks, containers, and front-end technologies.
| Category | Popular Options |
|---|---|
| Programming Languages | JavaScript (Node.js), Python, Java, Go, C# |
| Databases | PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB, Redis, Amazon DynamoDB |
| Back-end Frameworks | Express.js, Django, Flask, Spring Boot, ASP.NET Core |
| Containers | Docker, Kubernetes |
| Front-end Technologies | React, Angular, Vue.js, Svelte, Next.js |
Step 5: Crafting the Design
Refining the UI/UX design of your app is essential to make it intuitive and accessible. While A/B testing is a good way to refine the design, you should hopefully start off on a solid iteration already.
Here's a table of general recommendations for UI/UX design in cloud application development:
| Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Responsive Design | Ensure the application is fully responsive and works well on various devices and screen sizes. |
| Dark Theme | Provide a dark theme option to enhance user comfort, especially in low-light environments. |
| Intuitive Navigation | Design a clear and intuitive navigation structure to help users find information quickly and easily. |
| Scaling | Implement scalable UI elements to handle different amounts of content gracefully. |
| Whitespace | Use whitespace effectively to create a clean, uncluttered interface and improve readability. |
| Accessibility | Ensure the application is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities (use ARIA, etc.). |
| Consistency | Maintain visual and functional consistency across the application to provide a cohesive experience. |
| Performance | Optimize for fast load times and smooth interactions to enhance user satisfaction. |
| Feedback | Provide immediate feedback for user actions (e.g., button clicks, form submissions) to confirm activity |
| User Testing | Conduct regular user testing to gather feedback and make iterative improvements to the design. |
That’s why prior market research is so important. It cuts down on the number of times you’ll need to tweak the design, saving your budget.
Step 6: MVP Creation and Testing
Delivering the first working version of the product is the last point where you can reasonably request major changes. It’s your chance to really see your product in action, feel out its usability, and understand if it matches your expectations.
Here is a table with general recommendations for MVP (Minimum Viable Product) creation and testing in cloud application development:
| Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Define Core Features | Identify and focus on the essential features that solve the main problem for your target users. |
| User Research | Conduct thorough research to understand user needs and pain points to guide feature prioritization. |
| Quick Prototyping | Create wireframes or mockups to visualize the product and gather early feedback before development. |
| Agile Methodology | Use agile development practices to iterate quickly and adapt to changes based on feedback. |
| Cloud Infrastructure | Utilize cloud services for scalability, reliability, and ease of deployment during the MVP phase. |
| Automated Testing | Implement automated testing to ensure code quality and catch issues early in the development process. |
| Continuous Integration | Set up continuous integration (CI) pipelines to automate builds, tests, and deployments. |
| Feedback Loops | Establish channels for user feedback (e.g., surveys, analytics) to gather insights and improve the product. |
| Usability Testing | Conduct usability tests to identify and fix any user experience issues before wider release. |
| Monitor Performance | Use monitoring tools to track the performance and reliability of the MVP in real-time. |
| Scalability Planning | Plan for future scalability to ensure the MVP can handle increased load as user base grows. |
| Documentation | Maintain clear and concise documentation for developers and users to facilitate understanding and usage. |
| Launch Strategy | Develop a clear launch strategy, including marketing and communication plans, to attract initial users. |
| Iterative Improvement | Continuously gather feedback and iterate on the product to enhance features and address issues. |
At the MVP stage, thorough testing begins to make sure your app ships without any major errors or bugs.
Step 7: Launching the App
Not much can be said here beyond the obvious: your cloud app development should be fully ready for launch with rounds of QA, a prepared marketing campaign, and an estimation of your desired results.
Here is a table with general recommendations for launching an app in cloud application development:
| Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Pre-launch Testing | Conduct thorough testing, including beta testing, to identify and fix any remaining issues before launch. |
| Scalability | Ensure the infrastructure is scalable to handle increased user traffic and load during and after launch. |
| Performance Monitoring | Set up monitoring tools to track the app’s performance, uptime, and errors in real-time. |
| Backup and Recovery | Implement robust backup and recovery plans to protect against data loss and ensure quick recovery. |
| Security Measures | Enforce strong security practices, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. |
| Marketing Strategy | Develop and execute a marketing plan to promote the app and attract initial users. |
| User Support | Provide clear and accessible user support channels, such as helpdesk, FAQs, and live chat. |
| Feedback Collection | Establish mechanisms for collecting user feedback to make ongoing improvements. |
| Analytics Setup | Integrate analytics tools to track user behavior, engagement, and key performance indicators (KPIs). |
| Documentation | Ensure all user and technical documentation is complete and accessible. |
| Soft Launch | Consider a soft launch to a limited audience to gather feedback and make final adjustments. |
| Communication Plan | Prepare and communicate a clear launch plan to all stakeholders, including timelines and responsibilities. |
| Post-launch Support | Plan for immediate post-launch support to address any issues that arise quickly. |
| Community Engagement | Engage with the community through social media, forums, and other channels to build a user base. |
| Update Plan | Develop a roadmap for future updates and enhancements based on user feedback and market demands. |
Knowing your own metrics for success and the market situation will help you avoid setting your sights too high.
Post-Launch Best Practices
The following strategies will guarantee long-term success for your cloud application following its launch:
- Establish performance and uptime monitoring systems along with behavior tracking for users.
- Applications require scheduled updates that use user feedback and analytics results as decision-making criteria.
- Security logs should be monitored while vulnerability patches must be deployed directly after discovery.
- Business KPIs such as churn rate along with revenue per user and cost per acquisition should be monitored.
- Your team should keep records that benefit users and team members.
Costs of Developing Cloud Applications
The cloud-based app development cost commonly includes infrastructure expenses, developer tools, security measures, standard cloud application development expenses, and post-release maintenance costs, among other expenses. Let’s review them all and see where you can save money in each case.
Among the factors that make up the bulk of the expenses in terms of cloud app development costs, infrastructure comes first. You will be paying to your provider, with extra costs incurred depending on:
- Server instances
- Databases
- Storage space
In this case, it’s clear that you can save money by going with a cloud provider with better pricing or limiting the app scope. Using less storage and servers means spending less.
Next, you’re paying for developer tools. Most will have licensing fees for frameworks or libraries used in your project. You can limit these expenses by using open-source and free libraries, but that’s not always an option.
Security measures are also important expenses in cloud app development. You’ll be paying for SSL certificates, compliance certs, and other layers of protection like firewalls. You can limit spending by cutting down on the number of payments, but that could be a security risk.
Then, of course, you have the standard cloud application development expenses - designer, developer, and tester salaries. Another category where it’s best not to skimp on the cost, as these are the employees guaranteeing your product’s quality.
Lastly, it’s important to plan post-release maintenance in the budget, as updates, bug fixes, and monitoring tools will always be necessary. Including all possible deviations from regular cloud app development helps you be prepared for the worst, while working to create the best app.
Possible Challenges in Developing Cloud Applications and Ways to Mitigate Them
Here are some problems you could face during cloud application development and to address them properly.
Considering Interoperability
Every cloud provider is different, so it’s important to adapt your code to work on at least a few of them. This will allow you to keep the app portable and, thus, more useful. Sticking to cloud computing standards will take more time, but it’s key to ensuring the longevity of your product.
Performance Issues
It’s good to be familiar with your chosen provider and knowing where their data centers are. Also, it’s a good idea to conduct testing and see how your app performs specifically in that environment. Latency can be a big problem, and a poorly working product can’t carve out a niche in the market for itself.
Regular testing and monitoring are the answer here, as they help spot problems and ensure stable performance.
Scalability Troubles
On the surface, all providers will promise load tolerance and good scalability. However, when the time comes, user counts rise, and some may struggle to keep up with the demand. That is why it’s important to verify the provider’s claims of processing power. Another solution is to use a hybrid approach to cloud app development so that your structure doesn’t rely solely on one platform.
Why Should You Invest in Cloud App Development?
As a rising industry with plenty of room for everyone to succeed, cloud app development is a smart investment. By getting onto this trend early, you have the chance to be among the top players.
Cloud solutions are used in a variety of industries, too, so you won’t be constrained by having to cater to just one niche. This opens up room for experimentation and expansion.
How Can JetBase Help You With Cloud Application Development?
We’ve talked at length about the ins and outs of cloud apps, from what they are to their benefits and challenges. With all that said, you should now have a pretty clear and balanced picture of cloud app development. In fact, we’re hoping you’ve decided to take the leap and try it for yourself. However, handling complex cloud app development in-house can be costly and time-consuming.
JetBase would like to throw its hat in the ring as your cloud application development partner. Our team has more than 9 years of experience in the market, providing custom cloud app development services and developing cloud applications. The cases in our portfolio include some truly challenging yet successful cloud projects.
One of them is Grapevine. Built on AWS, this asynchronous team meeting software got accolades two years in a row on Producthunt, and for a good reason. This SaaS platform used audio and video messages to keep teams coordinated during remote work. We made sure to keep this communication accessible, using AssemblyAI to transcribe messages.
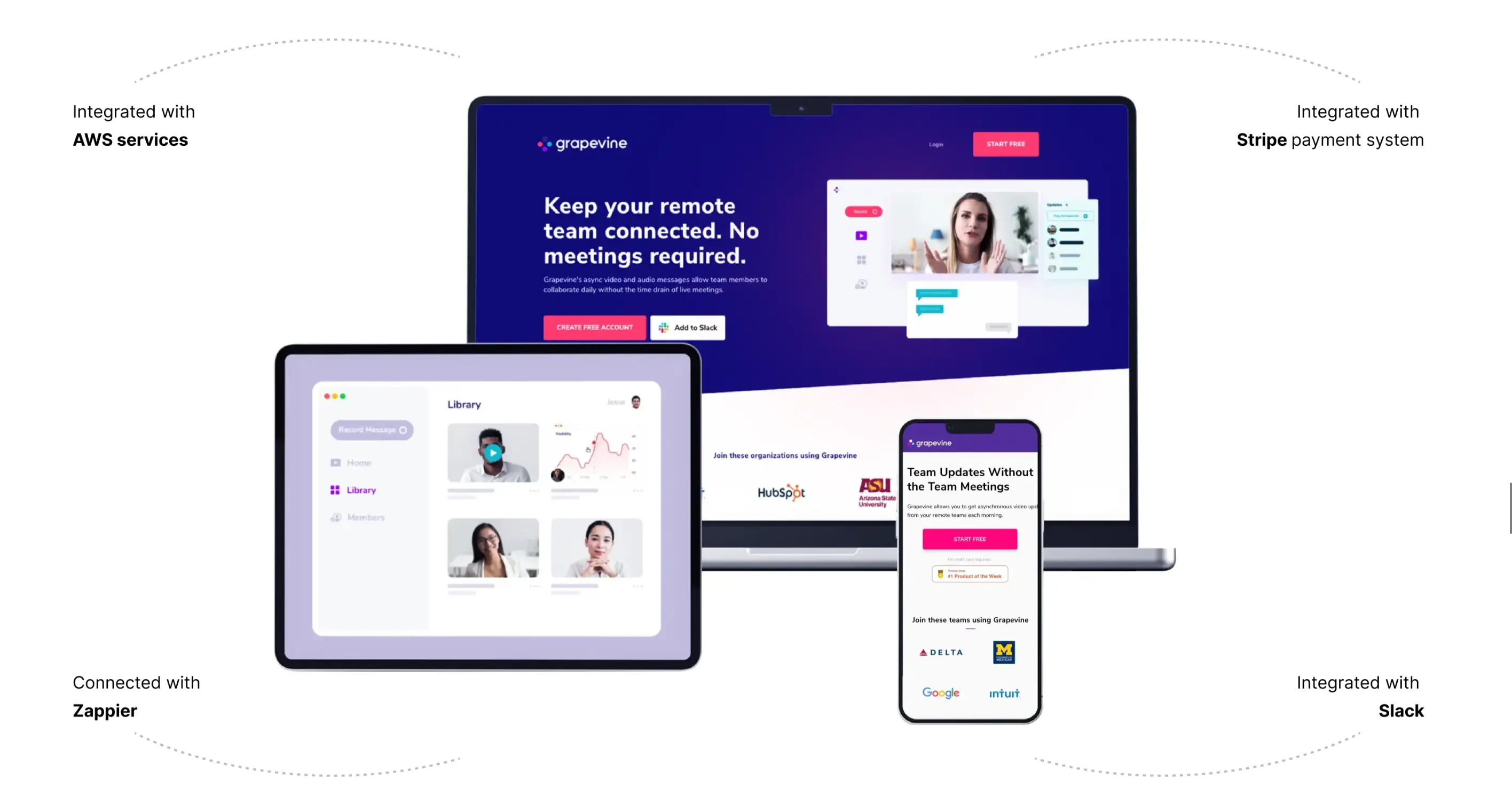
Then, we adapted Grapevine to any device with CloudConvert integration. This allowed users to view the platform and messages in any browser or device type. We also added Stripe and Slack integration to make sure teams could carry over information easily. All of this was backed up by AWS, ensuring stability and smooth operation.
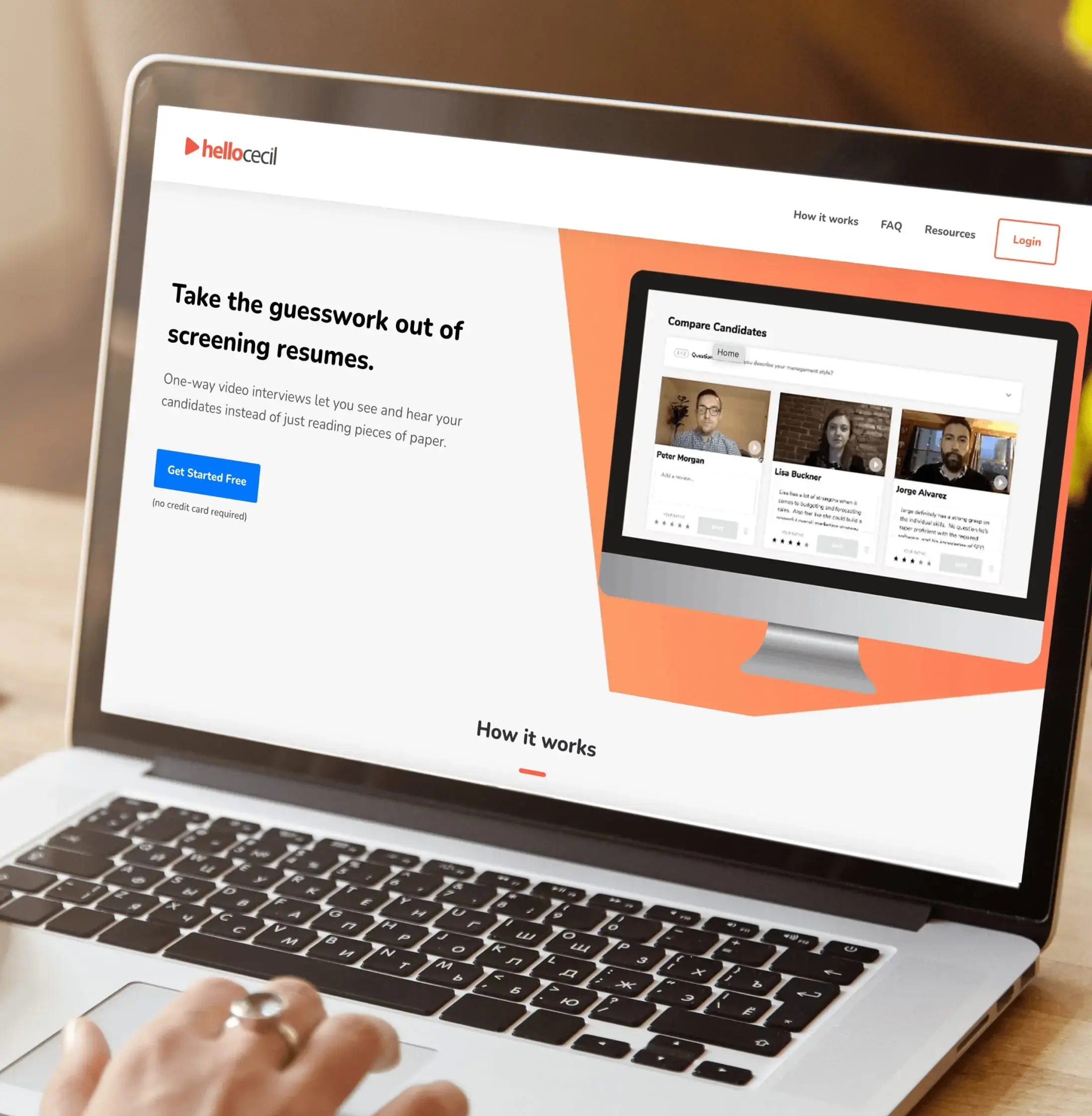
Another of our video-based products, Hello Cecil, used similar tech to upend online interviewing. Also lauded by Producthunt and built on AWS, this platform challenged us by requiring high-quality video streams with multiple users active at once. Building off of an MVP, our team used Ruby on Rails to create a refined, sleek application that ran fast.
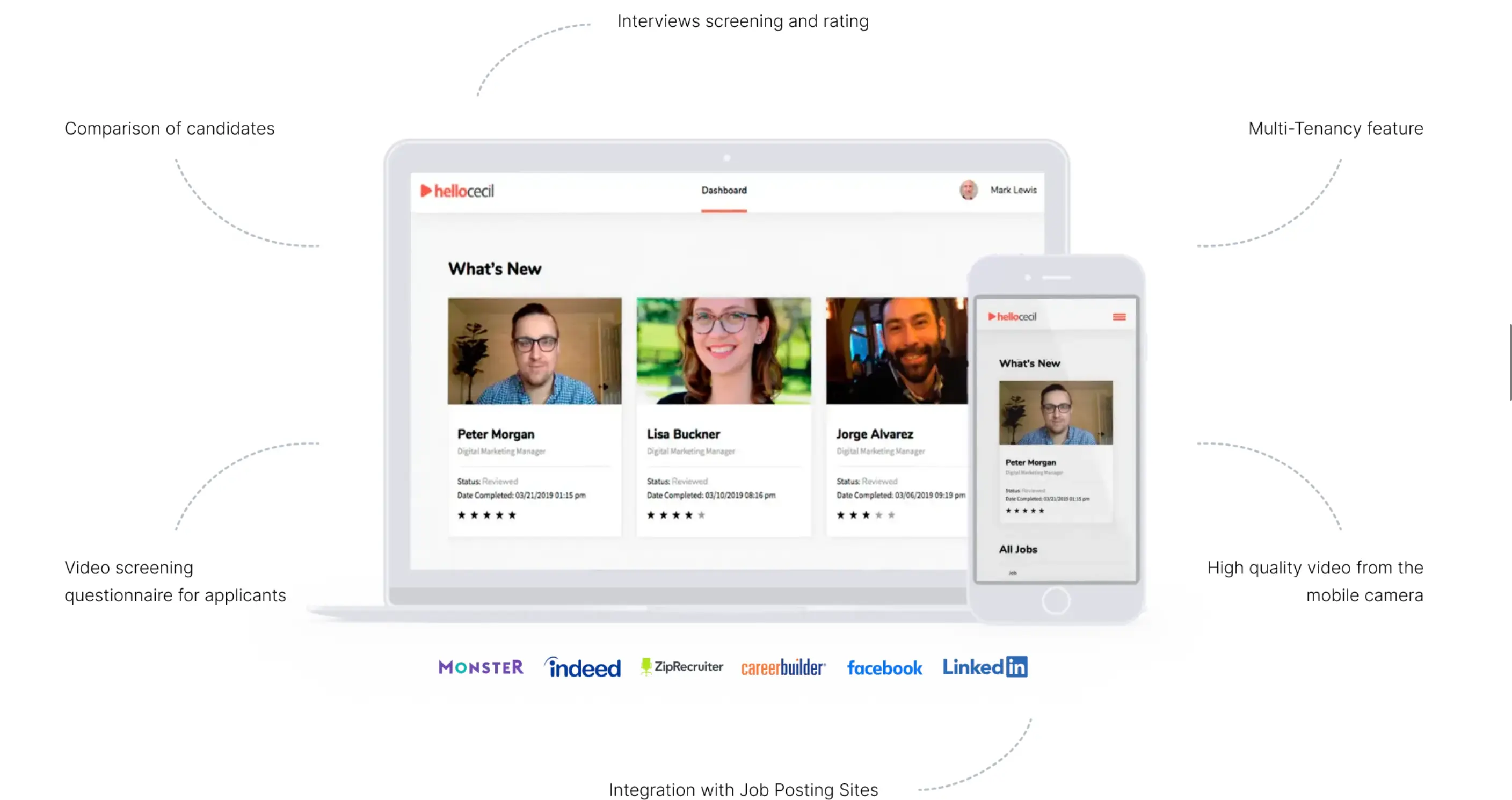
We integrated all the major job listing sites, such as LinkedIn, and made sure the application could be run without any additional software. This made it simple to pick up and use, opening up online interviewing even for job seekers who may not have interfaced with such technology.
While these are just two cases from our years of craft, we’d be happy to share more. If you want a quick consultation on cloud app development or to pitch us a project, we’re open to offers. Don’t hesitate to get in touch today.