Cloud computing and, consequently, cloud scalability have become a massive driving force worldwide, acting as the backbone of many businesses. For example, up to 42.5% of EU businesses were using the cloud in 2023 for anything from software hosting to storage. However, this level of popularity wouldn’t be anywhere near this without companies knowing how to leverage scalability in cloud computing.
Today’s guide will teach you all about scaling in cloud computing, from its types to its benefits. We’ll talk about what sets it apart from cloud elasticity and how to achieve high scalability. With these topics, we hope you will have a comprehensive picture of scaling a cloud infrastructure. Using JetBase’s experience with the cloud, we’ll cover the important points for you to know. Let’s begin!
What is Cloud Scalability?
Scalability in cloud computing refers to the cloud’s ability to manage resources according to the user’s needs. While most may associate it with growth, scaling works both ways. This means a business may want to use more or less storage, throughput, or computing power. It’s important to manage and adjust that usage to fit each use case.
Scalable cloud computing helps ensure businesses don’t overuse resources and incur excess costs by paying for resources they do not need. It also makes the cloud more accessible to users, adaptable to the client’s needs, and load-resistant.
How Does Cloud Scalability Work?
We’ve established what is cloud scalability and its associated terms. However, what matters most isn’t knowing about cloud scalability. It’s getting to the point where your cloud is up to snuff. So now it’s time to talk about ways to scale and do it efficiently and cost-effectively.
As with any project, research comes first. To enable scalability in cloud computing, you must find areas where you can actually scale up. Monitor your infrastructure and determine whether some processes are stalling due to a lack of resources. Looking for abnormal or suboptimal results is the key, as you’ll know what has to be changed.
Blindly adding resources may feel like a fix, but it’s a band-aid solution at best, as you can’t solve a problem without diagnosing it first. Once you figure out where to apply scaling, you can actually implement cloud scalability. We’ll expand on that in the respective section, but when it comes to the inner workings of the process, things are fairly straightforward.
To achieve scalability in cloud computing, you either increase available resources or distribute them more effectively. Note that “effective” won’t always mean “put everything on the core processes,” as sometimes, you need to reassess your priorities to keep the infrastructure running.
Types of Scaling in Cloud Computing
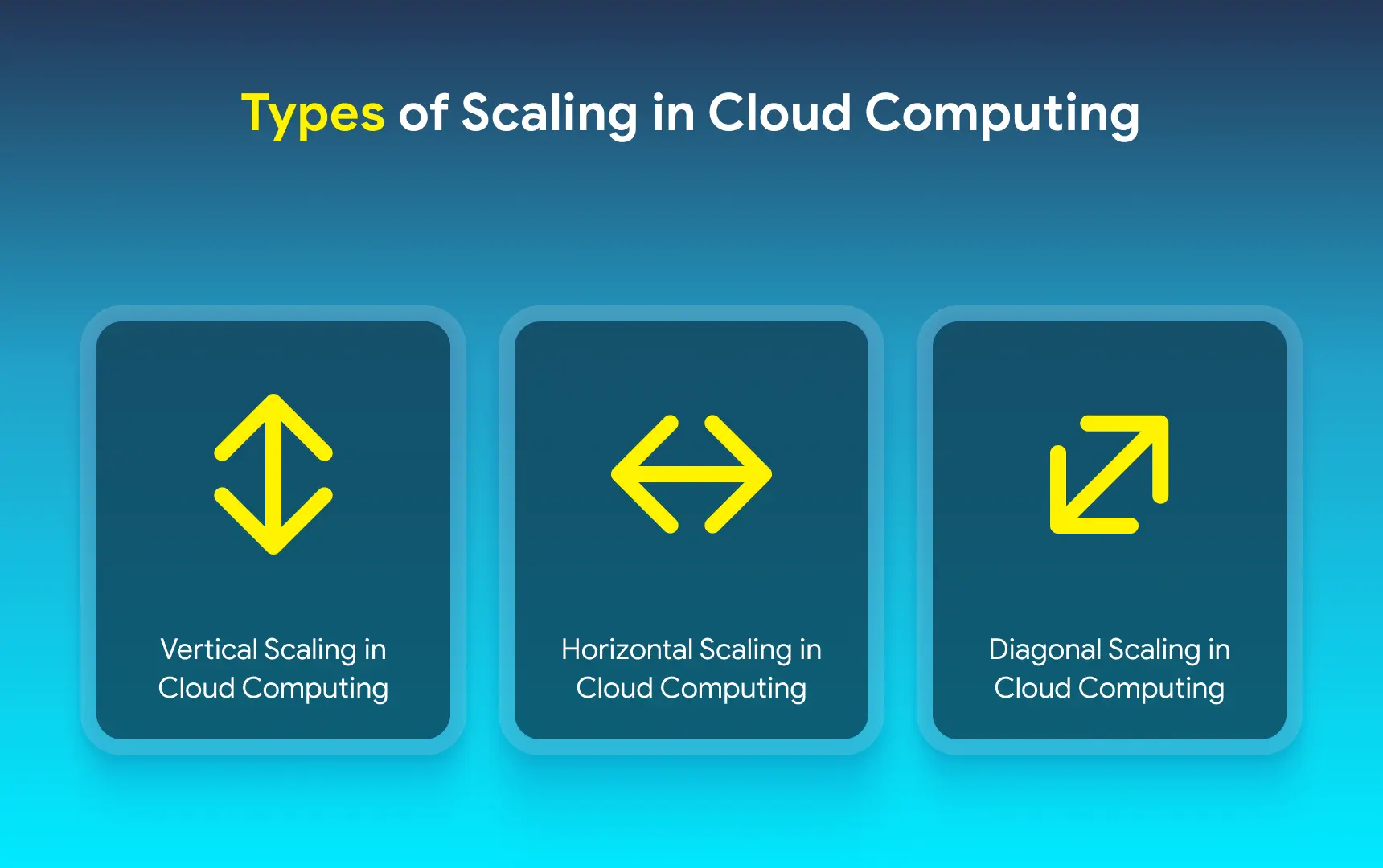
Achieving scalability is great, but you must know what kind you pursue. After all, the three core types of cloud scalability are not the same, and each has its own special points to focus on. Let’s discuss them one by one and highlight what separates them.
Vertical Scaling in Cloud Computing
Making a scalable cloud through vertical methods involves improving your servers and other hardware. This means adding components to increase RAM availability or storage space, thus obtaining more resources without buying more servers.
However, as you may guess, cloud scaling of this type has its limits. After all, you can’t endlessly increase one server’s capacity. But it’s also true that this is an effective method to a point, as it’s cost-effective and lets you achieve some cloud scalability with resources you may already have.
Horizontal Scaling in Cloud Computing
Like we said, vertical cloud scalability has its limits. So, if you can’t go higher, why not go broader, right? Horizontal scaling is about expanding how many instances (virtual machines or virtualized environments on physical servers) you’re running and getting more processing resources.
Thanks to this method, you can build a scalable cloud that withstands significant traffic and supports even the most resource-hungry applications. This approach depends mainly on how much you’re willing to spend, as horizontal cloud scalability requires substantial investments.
Diagonal Scaling in Cloud Computing
As you may guess from the name, this is a hybrid of vertical and horizontal approaches. It’s a combo that is used when you need a bit of everything: storage, processing, and throughput. As a result, it can be quite pricey as you’re buying components and instances simultaneously. However, the resulting scalability in cloud computing makes the cost worth it.
For these approaches, it’s important to consider what matters most to you and what your needs are likely to grow into. For example, you might scale vertically while you need storage, thinking you’re saving money in the long run. However, it’s smart to assess if you might need the scalability of cloud computing for other purposes as well.
![Cloud Software Development [AWS].webp](/static/Cloud_Software_Development_AWS_a351611d38.webp)
Cloud Scalability Types Comparison
As your business grows, you may find yourself needing more bandwidth or CPU instead of just storage. This will then require you to switch gears and try a different method for cloud computing scalability. In order to help you pick the right one, we’ll cover their differences in a simple table, letting you see which one best fits your needs.
| Type of cloud scalability | Vertical | Horizontal | Diagonal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Minimal investment, repeated expenses | High, cost-effective over time | High initial investment, potential to be cost-effective |
| Focus | RAM and storage | Bandwidth and CPU | Processing and storage |
| Maintenance complexity | Low (working with one server or few) | High (working with a multitude of instances) | High (likely multi-instance) |
| Limitations | One server’s capacity | Budget for adding new instances | Budget, as well as architecture |
Benefits of Scalability in Cloud Computing

It might sound like scaling your cloud is a lot of work, and you might ask, “What is scaling in cloud computing really going to get me for my efforts?” That’s a fair question, and thankfully, there are a few answers. It obviously requires skill to implement scalability in cloud computing the right way, but you won’t have trouble with that while JetBase is on your side.
Financial Stability
This is one of the main advantages of any improvements you make to your business, and scalability in cloud computing is no exception. While there’s an initial cost to it, building a scalable cloud lets you take on more clients, provide better services, and save money.
The former two points are pretty clear - more work with higher quality means more profit. For the third, though, it’s important to remember that your initial expenses will be recouped. Firstly, better hardware lasts longer, preventing the need for expensive maintenance. Then, there’s the fact that better servers prevent operational losses and improve your reputation among customers.
Stable Performance
What is scalability in cloud computing without higher bandwidth and the ability to support huge traffic loads? The whole aim of scaling your cloud is to make it withstand simultaneous usage by many apps and processes. Delving into cloud scalability lets you analyze and reinforce your system, raising its load resistance.
Higher Flexibility
Sometimes, having plentiful resources isn’t a blessing but a curse, as the excess has to be paid for, and nobody wants a higher bill. That is why flexibility is important for a scalable cloud. You can create tools that regulate resource usage, scaling it up or down, enabling lightning-fast reactions.
This means that you can meet customer demand head-on and provide scaling instantly, easily covering everyone’s needs. Putting thought into your cloud scalability protocols allows for on-demand support and provision, making your cloud a prime pick for users.
Stronger Security
A cloud with few resources available cannot sustain many simultaneous processes, which can leave gaps in its security. Conversely, a scalable cloud with plentiful optimization can run firewalls and monitoring software to detect and stop incoming threats. Thanks to that, you can keep user data protected while also guaranteeing the safety of your infrastructure.
Scalability vs. Elasticity
If you’re interested in scalability in cloud computing, you must have heard the term “cloud elasticity” before. Some may even confuse the two, using that term and “cloud scalability” interchangeably. That would be a mistake, though.
It is impossible to talk about elasticity without highlighting its difference from scalability. The latter implies a cloud’s potential to expand and improve, gaining more resources to work with. But elasticity isn’t synonymous with that, as it actually refers to a system’s ability to adapt. When you push your scalable cloud, does it adjust well? If so, you’ve got an elastic cloud.
Elasticity is reachable following the same practices we use to reinforce cloud computing scalability. Setting up automatic checks and protocols, expanding a cloud’s access to resources, and focusing on load balancing will all make your cloud more elastic. It can respond to higher loads without sacrificing performance or deprioritizing specific apps.
Therefore, high elasticity is a direct consequence of reinforcing your cloud scalability. So, if you want your cloud to accommodate multiple processes or resource-heavy apps, you know what to do. Or, perhaps, you will know once you read the next section.
How to Achieve Cloud Scalability?
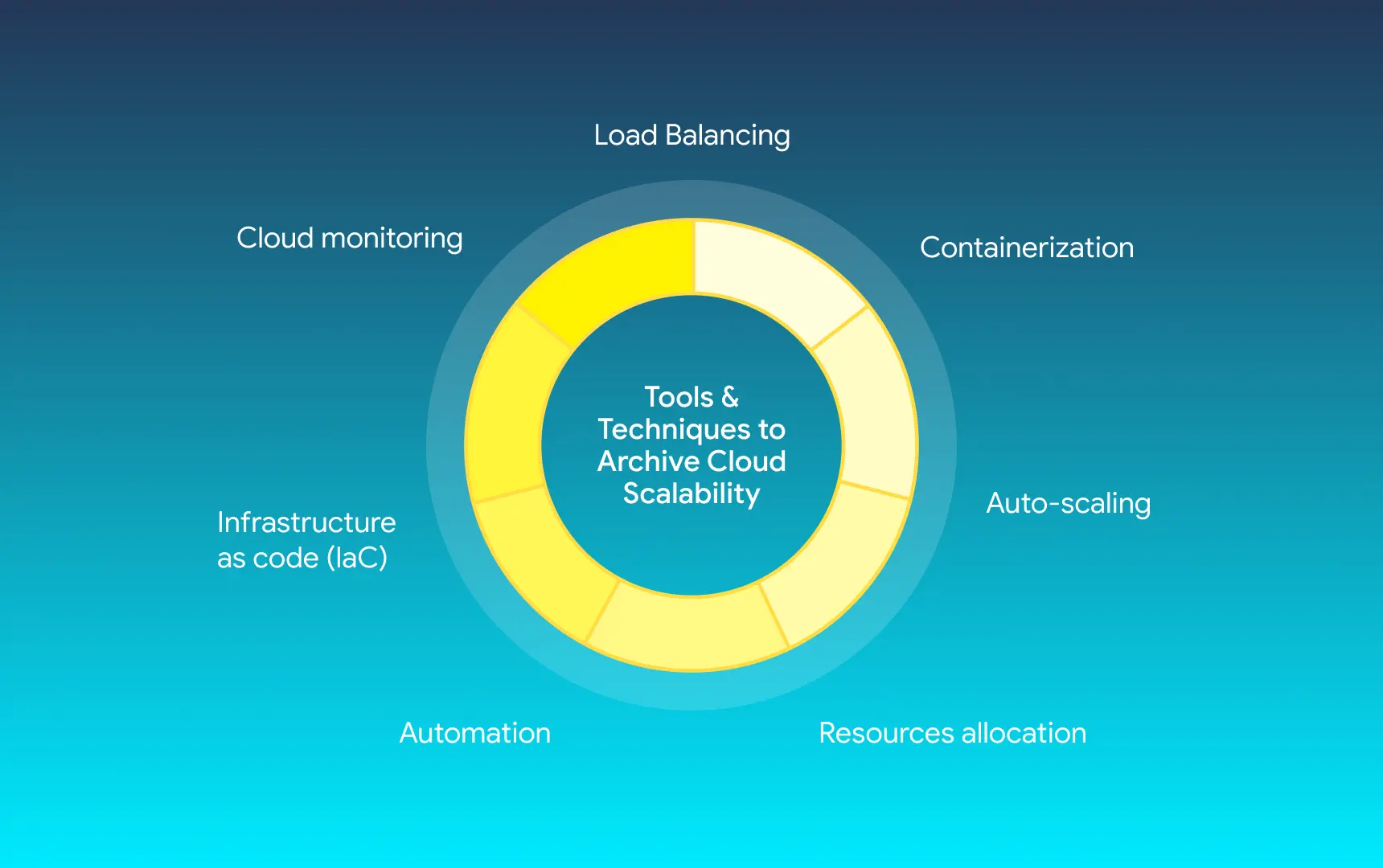
Knowing what is scalability in cloud computing is one thing, but it’s even more important to know how to achieve it. Here are some essential practices that will help you do just that:
- Load balancing;
- Containerization;
- Automatic protocols;
- Infrastructure as Code;
- Extensive monitoring.
Load Balancing
The first step for scalable cloud computing is load balancing, which works by spreading the incoming load or traffic across a variety of servers. This helps ensure that you’re not using up all the resources of one server and that processes can run smoothly regardless of load factors.
Containerization
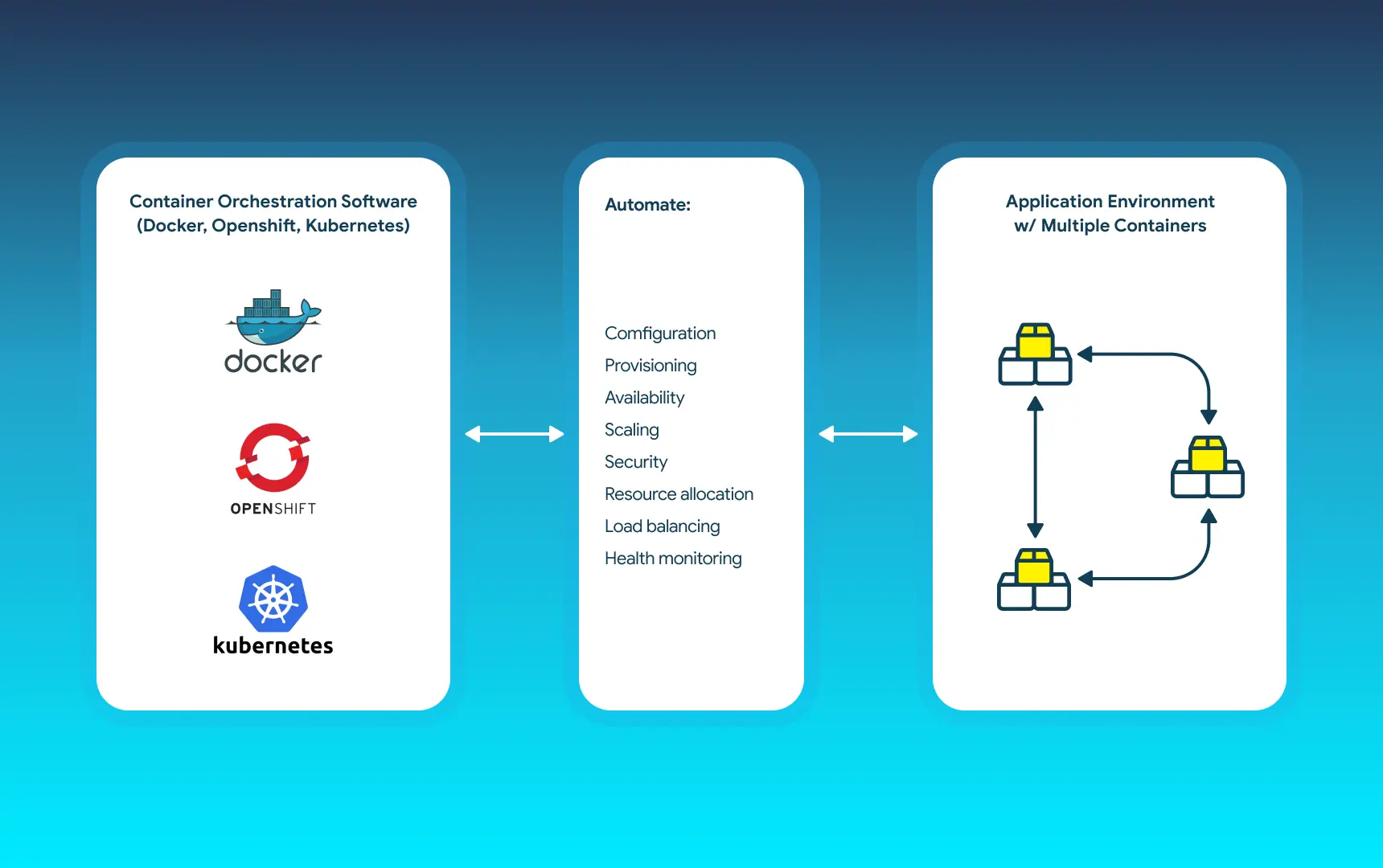
Next, splitting processes and apps into independent containers allows you to limit resource use for each separate container. This way, you can allocate enough for each application without affecting any others, simplifying cloud scaling and resource management.
Automatic Protocols
Third, automating scaling protocols and deployment processes can help establish more efficient resource allocation with minimal human input. Your cloud scaling will adjust based on which processes are launched, and the condition presets you chose earlier.
Infrastructure as Code
It’s also possible to rely on IaC, which speeds up infrastructure deployment. Thanks to that, you can nearly instantly deploy more resources to support apps. It does require work on the cloud’s architecture, but the resulting scalability in cloud computing speaks for itself.
Extensive Monitoring
Last but not least, monitor your cloud to determine peak load times and spot processes that aren’t using resources efficiently. Thanks to that, you can not only establish the aforementioned automation protocols but also understand your system's flaws.
However, combining the above ideas truly works for cloud computing scalability. The only meaningful way to scale is to create a complex suite of measures that regulate your cloud’s resource use. This creates a more sustainable ecosystem and promotes lasting, cost-effective cloud scalability.
How Can JetBase Help You With Cloud Scalability?
After reading our guide to scalability in cloud computing, you know that JetBase has the theoretical knowledge to make your cloud more resilient. That expertise came through extensive work with cloud solutions. We’ve helped build modern SaaS products and optimized solutions to refine their interactions with the cloud.
Through it all, we’ve learned how to navigate cloud computing and optimize cloud scalability to accommodate any use case. This, coupled with our decade in the market and extensive research of modern technologies, makes JetBase the perfect vendor to scale your cloud. Our team is eager to reach new heights, so we treat every project with care and respect.
Thanks to excellent communication skills, broad and deep expertise, and a research-first approach, JetBase always delivers above expectations. If you want to see the optimal results of scalability in cloud computing, look no further. Just send us a request, and we can start our collaboration.