IoT or Internet of Things is a booming trend, slated to keep rising in value, up to $12.6 trillion in 2030. These devices work across a variety of industries with use cases ranging from boosting harvests to improving customer satisfaction rates. However, among all these, the healthcare industry is, perhaps, the most involved with IoT.
Today’s article will introduce the typical use cases for IoT in medical environments, address the challenges of IoT in healthcare, and showcase solutions for these typical problems. We’re aiming to highlight the value of this technology without handwaving users’ concerns. As a result, you’ll be able to see a clear path toward using IoT effectively. Let’s begin.
What Is IoT in Healthcare?
Before we proceed to the challenges of IoT in healthcare, let’s talk about exactly what IoT means in this industry and how it’s evolved. Initial IoT devices were pretty limited compared to the current crop, mostly used as basic sensors to track patients’ vitals. Relevant research suggests that this generation of devices had some substantial issues to address.
Thankfully, modern IoT is much more diverse and applied to a range of medical processes. This still includes sensors, ones that now operate in remote scenarios, using 5G networks to establish 24-hour data collection for patients with chronic conditions. Similarly, IoT-enabled assisted living machines are literal lifesavers and rely on special protocols to control their performance.
In general, IoT centers around making “smart” devices that can replace human observation and ensure more precise, constant processing of medical data. We’ll talk about this in more detail right below, but for now, we’d like to round out this section by highlighting scientific opinion on IoT.
Current papers describe this technology as nothing short of revolutionary, though they also point out the ongoing expectation of more security for such devices. While none of us can see the future, the recent history of IoT devices seems to indicate movement toward that goal.
Common Uses for IoT in Hospitals and Clinics
We’ve already touched briefly on potential applications of IoT devices in medical environments, but it’s good to have a more precise idea of why IoT is such a force of nature. This way, you will easily see why they’re worth overcoming the challenges of IoT in healthcare. Let’s start off with a simple one — remote patient monitoring.
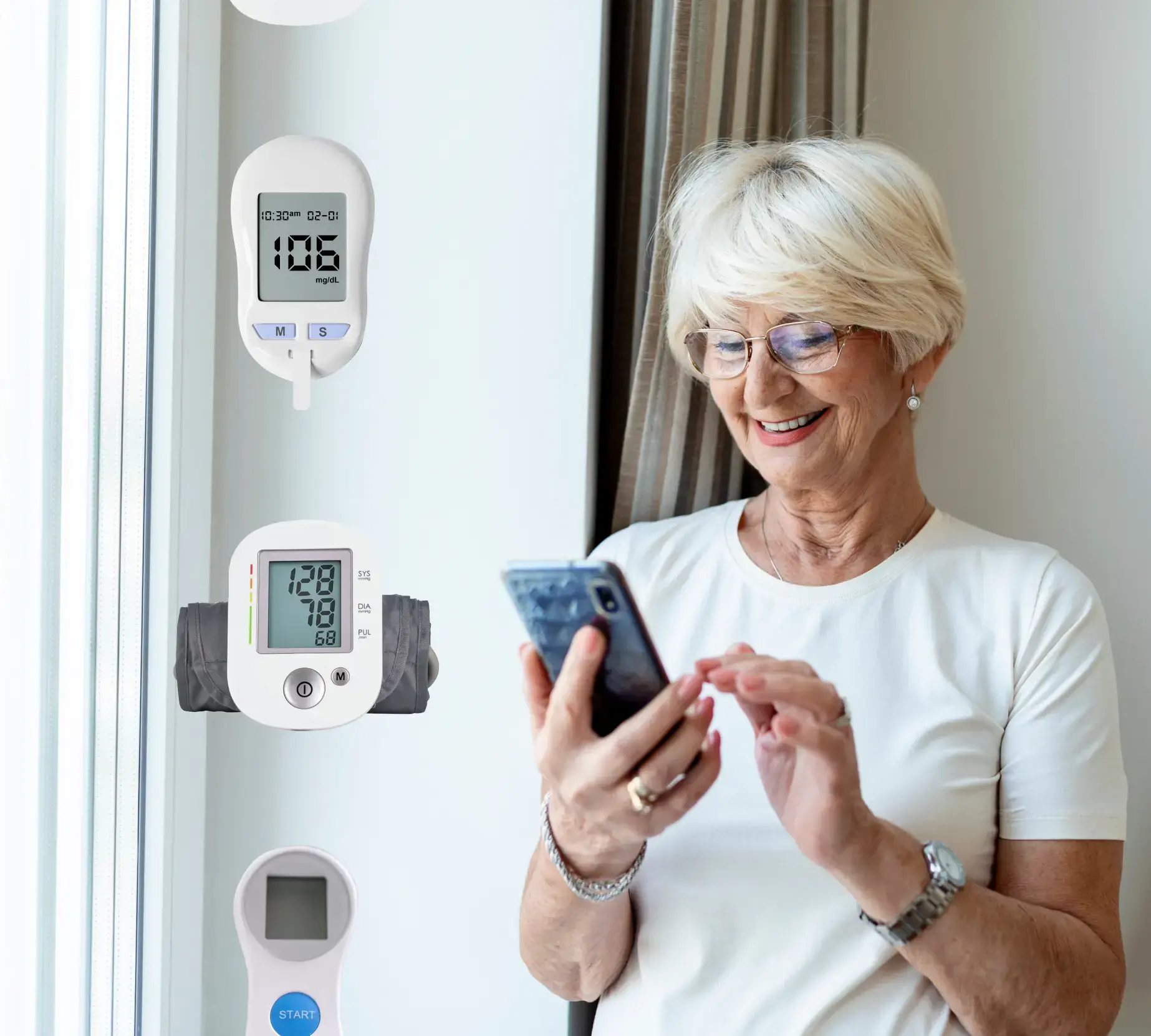
Millions of people around the world suffer from chronic and long-term conditions that require more care than a typical bout of flu. Such issues are easier to manage when their doctor has unlimited access to the patients’ vitals and can spot even the slightest problems right away. This can also be automated with the use of algorithms that detect anomalies and early warning signs.
Monitoring can include data like glucose levels, blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and more. It can also allow patients to use self-reporting to efficiently track things that a sensor can’t measure. This means IoT devices can be helpful in measuring people’s mental health and pain levels, aiding them in recovery.
For something more exciting, look toward robotic-assisted surgery, where surgeons can perform remote operations or rely on robo-assistants, who don’t pose any contamination risks. In fact, there already is a case of a robot performing the entire surgery solo.
Yet another futuristic application is the availability of ingestible sensors, which are basically little pills that patients swallow. Once inside the body, they collect and transfer health data with non-invasive methods. This can be a real game-changer for post-surgery recovery, ensuring that nothing is going wrong internally for a patient.
| Use | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote monitoring | Gathering health data and processing it automatically with simple sensors. |
| Robo-surgery | Autonomous assistants that can aid human surgeons or, soon, perform surgeries themselves. |
| Ingestible sensors | Internal vitals tracking with bleeding or rupture detection. |
| Wearable trackers | Fitness aides that can track workout performance and vitals during high-activity periods. |
| Pill intake control | Automated reminders about medication, confirmation that patients are sticking to their health routines. |
Data Privacy and Security Challenges of IoT in Healthcare
Not everything about using IoT in medical processes is perfect, of course. We’ll cover the disadvantages of IoT in healthcare in multiple sections, separated into their “themes”. This will include:
- Privacy and security issues;
- Integration challenges;
- Legal concerns;
- Technical issues.
Now, let’s start with questions of data privacy around IoT integration.
How IoT Puts Patient Data at Risk
Challenge: The fact that patient data is involved makes this one of the most pressing challenges of IoT in healthcare. The usage of third-party devices is already, technically speaking, a risk, though most IoT developers will have a pristine reputation that addresses that. However, the data that IoT devices gather has to be well-secured, or you run the risk of a breach exposing all of it.
Therefore, the main worry here is how reliable your databases are and whether the transit protocols on your devices are secured according to the latest standards. Plus, there must be procedures related to data deletion and sharing, following strict protocols.
Solution: The challenge itself presents some obvious paths to address it. For example, if database security and protocol reliability are in question, you just need a team to reinforce them. This can involve encryption and specific code to prevent injections, including MiTM attacks, and, of course, more sophisticated authentication methods.
Similarly, data that’s been gathered and processed should only be accessible to those with the right clearance and should never be stored longer than necessary. There’s no need to keep extensive information on every case for years, at least not in the form of raw health data.
Compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and Other Laws
Challenge: Legal compliance is a tricky subject as it’s wholly dependent on the jurisdiction in which a business operates. Talking about the legality of certain data-related practices in medicine often focuses on legislation like HIPAA and GDPR, but those don’t affect everyone. Large chunks of the world, such as countries in Africa and Asia, have very different laws and limitations.
It’s also important to remember that a business that’s compliant with HIPAA in 2025 won’t necessarily be compliant with it after it gets updated. So all internal systems must be monitored and verified to still be up to the current standards.
Solution: First things first, your legal consultants or in-house team will need to assess which laws your operations must adhere to. This can vary based on your location, the types of services you provide, and the kinds of equipment used. IoT devices rely on data collection, processing, and temporary storage, which make them relevant to both HIPAA and GDPR.
Typically, laws will require that you provide people with the ability to see their health data and request that it be deleted. It’s an important aspect of data management, and your internal systems should provide the corresponding controls for that very purpose. Realistically speaking, you should not be facing too many such requests, but being ready for them is vital.
Device Hacking and Network Security Issues
Challenge: While IoT technology is constantly evolving, not every healthcare business or institution will have the funds for the latest models. It leaves them in a precarious position, as older devices could have unpatched security vulnerabilities. As a result, hackers may gain access to them or fully take over, disrupting functionality and leaking data.
In a similar vein, many hospitals run legacy systems, exacerbating the challenges of IoT in healthcare by leaving them reliant on insecure networks. The result is multiple points of failure that could allow bad actors to gain internal access and take over the ecosystem entirely.
Solution: If the budget allows, always keep pace with the latest developments in the IoT world and use the best models available. Additionally, make sure to keep the firmware up to date, installing any patches as soon as they are released. This obviously applies to security updates the most, but it’s a generally important practice regardless of the patch content.
As for networks, you would ideally keep your system modernized to avoid any possibility of security gaps, but that can be a challenge. However, regardless of the software and hardware you run, it’s important to ensure encryption at rest and in transit. You should also ensure that all points of access have measures in place to prevent unauthorized changes and operations.
Integration and Compatibility Problems
Speaking of old networks, they can also create challenges of IoT in healthcare through issues with network integration or scalability. These are just as important to deal with as typical security roadblocks, because you can’t get the full extent of usability out of IoT otherwise.

Disconnected Devices and Systems
Challenge: IoT lives and dies on the availability and quality of data, because an IoT device that doesn’t deliver plentiful information is just a fancy gadget with no purpose. However, due to how complex systems can get, it is possible to lose connection between certain devices. Therefore, it’s in the company’s interest to ensure connection stability and keep IoT integrated well.
Solution: The answer to these challenges of IoT in healthcare is to look at the big picture when adding IoT devices into your ecosystem. You must ensure their connectivity protocols are compatible with your other hardware and that their data transfer capabilities match up. Plus, it’s important to establish alternative connection opportunities with reliable APIs that will ensure that a single failure in the system won’t disrupt data processing.
Problems with Scaling and Updating IoT Solutions
Challenge: As your business grows and the number of patients increases, IoT devices in your network will have to shoulder an increasing amount of traffic. This can be challenging both because expanding your roster can be expensive and since improperly configured devices won’t support such scaling.
Solution: The best way to guarantee your IoT system will scale with your growth and needs isn’t to just buy more devices, of course. Instead, configure them in ways that maximize resource use efficiency, with smart queueing and bottleneck prevention.
This can mean establishing a cloud network with third-party platforms, which would offer a boost to processing speeds and free up enough capacity to avoid any stoppages. It does create additional expenses, but it’s the best way to ensure your IoT network’s healthy growth.
Legal and Ethical Challenges of IoT in Healthcare
Some IoT challenges in healthcare transcend internal processes and move into the realm of legality, as well as ethical questions. Although some of these may be more of interest to your legal team, they are still important to understand and address when they come up. The two major points that a business will have to consider are liability and ethical data processing.
Challenges with Patient Consent and Data Use
Challenge: Just because a patient might need to use an IoT sensor to track their vitals doesn’t mean they’ll want to agree to it. It’s counterintuitive, sure, but not everyone will be comfortable with unfamiliar technology. Moreover, even if the patient does agree, you might be violating some ethical boundaries unless you’ve properly and fully informed them about the device.
Solution: Providing in-depth informational materials can be a good first step toward educating patients about IoT and solving these ethical challenges of IoT in healthcare. It allows them to make decisions based on their understanding of the tech and the usage of their data. This way, you can be sure that the consent is fully informed and would hold up in case of any unforeseen circumstances.
Who’s Responsible When IoT Devices Fail?
Challenge: Accidents happen, and IoT devices aren’t immune to disruptions or faulty quality control. While most cases of failure should only result in a bit of missing data, failure can be much more dangerous with devices like robo-assistants or ingestible sensors. In any event, an IoT device causing serious issues may lead to legal action and the need to investigate that occurrence.
If such a thing happens, it is important for a medical institution to be able to offer an explanation of the error and confirm that it didn’t occur through any fault of theirs. This protects you from lawsuits and can help avoid such issues in the future.
Solution: Always keep extensive logs on all IoT devices and their performance, collecting analytical data. This will not only help understand the cause of failure but could also help in boosting their efficiency over time. If a failure does occur, analyze the available information and contact the manufacturer to report the issue.
This is particularly important if the fault turns out to be with the device itself, as it may allow them to fix the problem and help other businesses avoid these challenges of IoT in healthcare. Generally speaking, though, it’s important to do regular maintenance and keep the device firmware up to date in order to prevent even minor failures. A well-maintained system won’t run into nearly as many issues as an “unkempt” one.
Technical Challenges of IoT in Healthcare Environments
Lastly, let’s discuss the roadblocks presented by hardware when it comes to IoT usage. There are two core issues that pop up the most often, and we’ll help you address them.
Poor Connectivity and Network Failures
Challenge: Poorly configured APIs and low throughput can lead to disruptions between IoT connections, leading to lost data. As we’ve established above, this can be a serious issue and result in lawsuits.
Solution: These challenges of IoT in healthcare are solved by investing in better infrastructure, including cloud platforms for 100% uptime and extra resources. It’s also important not to get complacent, running outdated systems, whether with old software or insufficient throughput for your current scaling levels.
Short Battery Life and Power Limitations
Challenge: IoT devices with weaker batteries require more frequent charging, which makes it necessary to have more backups or sacrifice valuable data collection and operation time. Similarly, limited power sources can considerably lower your ability to run an array of IoT devices, cutting into the hospital’s monitoring capabilities, for example.
Solution: Aside from the obvious solution of buying device models with higher battery capacity, which can be prohibitively expensive, there are a few other ways to deal with this. For one, you can extend battery life with smarter use, only enabling the device when it’s needed. This beats an always-on policy and can be automated in many cases. Lastly, look into renewable energy sources, which may be installed on the premises and help boost power production.
How to Overcome the Main IoT Challenges in Healthcare
Before we end our guide, we’ll round up the tips we shared above into a few general moments of advice. This little cheat sheet will serve as a good starting point for introducing IoT into a medical ecosystem effectively.
Strengthen Data Protection and Cybersecurity
Most challenges of IoT in healthcare center around security, so it’s only logical that you can solve them by investing time and resources into boosting your protection measures. Sometimes this can mean establishing a closed ecosystem where you have full control of the data. Other times it’s just about updating encryption protocols or adding extra authorization layers.
Choose Devices That Follow Standards and Work Together
As for the integration and compatibility challenges of IoT in healthcare, they can be alleviated by sourcing hardware that works with other parts of your system right away. It’s easier to achieve if you build from scratch, but even existing infrastructure may work with proprietary technology. Most importantly, always ensure that the devices aren’t just compatible but also don’t cause any security issues when combined.
Build Scalable and Reliable IoT Infrastructure
Create separate, secure databases that only host IoT data, backed up on a reliable cloud platform, piggybacking off its resources for extra security and scaling. We also highly recommend optimizing your IoT processes to prevent idling and eliminate any chance of failure. This is where your infrastructure team should put in the work and help establish a favorable system for IoT to deliver on its potential.
How to apply IoT in Healthcare?
This rounds out our guide to IoT challenges in healthcare and the best ways to deal with them. There can be a lot of work involved in ensuring full legal compliance and establishing resilient networks that can process data and keep thousands of devices connected at once. But with our tips and your own experience, the process becomes less intimidating.
If you still feel like you could use more help, JetBase is happy to lend a hand. We have spent more than a decade creating custom solutions and building reliable platforms for businesses. Our portfolio includes multiple healthcare cases, representing our team’s versatile experience and dedication to quality.
So whether you need a bit of professional consulting or engineers to round out your own internal team, JetBase is the right choice. We pride ourselves on diligent work that puts the client first and a flexible approach to collaboration. Try it out for yourself — all you need is to get in touch.